CONCRETE DEGRADATION

Concrete can present various degradation problems which reduce its durability and resistance. The main ones are:
–descaling with loss of lime by hydrolysis, consequent increase in capillary voids, predisposition for cracking along the reinforcements and reduction of mechanical strength
–sulphatic attack of magnesium which produces swelling;
–carbonation which leads to the formation of calcium bicarbonate with lower characteristics than the original matrix;
PROBLEMS : superficial detachments, swellings and cracks
SURVEY TECHNIQUES: cracks pattern analysis, carbonation analysis, chloride research
REINFORCING BARS CORROSION

By means of a specific electrochemical process an anodic reduction takes place and a consequent cathodic deposit of rust with reduction of the useful section of the reinforcement and formation of swelling of the concrete (spalling).
PROBLEMS: superficial detachments, swellings, cracks and cracks
SURVEY TECHNIQUES: corrosion analysis
HARDY SLABS INTEGRITY

Hardy slabs can present important mechanical resistance problems.
PROBLEMS: deformations and subsidence
SURVEY TECHNIQUES: sonic analysis, endoscopy, load tests, pacometers
CRACKS

all masonry and reinforced concrete structures can present injuries due to thermal, static and dynamic phenomena.
PROBLEMS: surface injuries, detachments, infiltrations
SURVEY TECHNIQUES: CONCRETEcrack pattern analysis, deformometry, thermal monitoring
INFILTRATIONS

Buildings and structures can present problems of waterproofing or disposal of rainwater.
PROBLEMS:humidity, spots
SURVEY TECHINIQUES: thermography, surface and internal temperature and humidity measurements
THERMAL BRIDGES
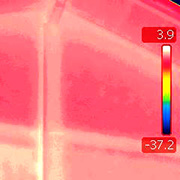
The thermal insulation characteristics of buildings represent the fundamental component for the realization of living comfort.
PROBLEMS: energy consumption, humidity, stains
SURVEY TECHNIQUES:
thermography, surface and internal temperature and humidity measurements
FIRE

L’incendio, nel caso delle strutture in cemento armato, può portare ad una riduzione non immediatamente evidente della sua resistenza meccanica.
PROBLEMI: distacchi, riduzione capacità portante
TECNICHE DI INDAGINE: sclerometria, analisi sonica, microscopio ottico